Elements of Information Security
Informationsecurity is defined as: "a state of well-being of information and infrastructure in which the possibility of theft, tampering, and disruption of information and services is kept low or tolerable."
It relies on the five major elements of: confidentiality, integrity, availability, [authenticity, and non-repudiation].
| Security Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Confidentiality | Confidentiality is the assurance that the information is accessible only to those authorized to have access. Confidentiality breaches may occur due to improper data handling or a hacking attempt. |
| Integrity | Integrity is the trustworthiness of data or resources in terms of preventing improper and unauthorized changes, the assurance that information can be relied upon to be sufficiently accurate for its purpose. |
| Availability | Availability is the assurance that the systems responsible for delivering, storing, and processing information are accessible when required by authorized users. |
| Authenticity | Authenticity refers to the characteristic of a communication, document, or any data that ensures the quality of being genuine or not corrupted from the original. The major roles of authentication include confirming that the user is who he or she claims to be and ensuring the message is authentic and not altered or forged. Biometrics, smartcards, and digital certificates are used to ensure authenticity of data, transactions, communications, or documents. |
| Non-Repudiation | Non-repudiation refers to the ability to ensure that a party to a contract or a communication cannot deny the authenticity of their signature on a document or the sending of a message that they originated. It is a way to guarantee that the sender of a message cannot later deny having sent the message and that the recipient cannot deny having received the message. |
The Security, Functionality and Usability Triangle
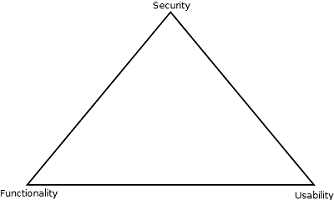
The level of security in any system can be defined by the strength of three elements: Security, Functionalit and Usability
Moving e.g. towards Security means less Functionality and Usability.
Functionality = Features
Usability = GUI
Security = Restrictions